Prices
In Drupal Commerce, a Price consists of a number and a currency code and is represented as a Price value object with two properties:
- Number: a decimal number, stored as a string.
- Currency code: a three letter currency code, stored as a string.
For example, here's how to create a Price with the value of 5 US dollars
$my_price = new Price('5.00', 'USD');
Important: note that the number value is actually a string. Why? Because when you're dealing with money, accuracy is critically important. These Stack overflow pages provide explanations:
- Why not use Double or Float to represent currency?
- Why don't applications typically use int to internally represent currency values?
When working with prices, you should use the Price value objects and methods instead of converting back and forth between strings and floats to use built-in +-*/ operators.
The Price class provides the following arithmetic and comparison methods, all of which rely on the helper methods provided by the Calculator class:
- add
- subtract
- multiply
- divide
- compareTo
- isPositive
- isNegative
- isZero
- equals
- greaterThan
- greaterThanOrEqual
- lessThan
- lessThanOrEqual
For example, if we want to add $10.00 to our $5.00 example Price created above, we can do this:
$new_price = $my_price->add(new Price('10', 'USD'));
And we can compare those two Prices like this:
if ($new_price->greaterThan($my_price)) {
// do something.
}
For full documentation of these methods, see Drupal\commerce_price\Price and Drupal\commerce_price\Calculator in the Drupal Commerce Price module. Also, the Drupal\Tests\commerce_price\Unit\PriceTest test code provides comprehensive example code for these methods.
Also note than when working with more than one Price, the prices must be in the same currency. You can convert a Price from one currency to another using the Price::convert() method. If you attempt to perform arithmetic operations or compare prices with different currencies, you'll get a CurrencyMismatchException.
Price Rounding
Drupal Commerce provides a service for rounding a Price to the correct number of decimal places, based on its currency. By default, a half value will be rounded up, making 1.5 into 2. Optionally, any of the php rounding mode constants can be used. See the php round() documentation for additional information.
Rounding service example: round $3.3698 to $3.37
$rounded_price = \Drupal::getContainer()->get('commerce_price.rounder')->round(new Price('3.3698', 'USD'));
if ($rounded_price->equals(new Price('3.37', 'USD'))) {
// This is true.
}
Price Fields
The Commerce Price module defines a Price field type which is used within Drupal Commerce for product variations, orders, order items, and payments. These fields store a Price value, as represented by number and currency strings.
Product prices
Product prices are associated with individual product variations, not with the parent product entities. See Product informatation structure for an explanation of the differences between products and product variations. Product variations have two price fields:
Priceis a required field; it is the default price value that is transferred to the order when the product variation is added to the cart.List priceis an optional field that is hidden by default. It is meant for display only and is usually crossed out in some way.
Both these price fields can be resolved, meaning that their values can be calculated automatically to support multicurrency or other complex pricing needs. See the Price resolvers documentation for more information on this process.
Additionally, the Commerce Pricelist module supports creating price lists for different dates, stores, individual roles or users. Each price list holds prices for different purchasable entities and quantity tiers. Prices can be defined manually or imported from CSV.
Order and order item prices
An Order has two Price fields: Total price and Total paid.
The total price for an order gets updated automatically whenever order items or Adjustments are updated for the order. The total price takes into account both the prices of the order items and all adjustments that are included in the price. The getTotalPrice() method returns this value. If you are looking for just the sum of order item prices without adjustments, you can use the getSubtotalPrice() method to calculate that total.
The total paid value, getTotalPaid(), is the sum of all payments made on the order. You can use the getBalance() method to get the difference between the total price and the total paid for the order. The isPaid() method will return TRUE if the order balance is less than or equal to zero.
An Order item also has two Price fields: Total price and Unit price.
The total price value is the product of the order item unit price and the order item quantity, rounded to the correct number of decimal places (based on the currency of the unit price). It is recalculated automatically whenever the unit price or quantity is updated or the order item is saved. This value does not take into account any adjustments on the order item. The getTotalPrice() method returns this value. You can use the getAdjustedTotalPrice() method to get the adjusted total price, which is also rounded based on currency.
The value for the Unit price, getUnitPrice(), for an order item can be set in a variety of ways throughout the shopping and order management processes. If you want to have complete control over its value, you can set the Overridden unit price boolean field value for an order item to TRUE. This can be done by administrative users through the order admin UI or programatically using the setUnitPrice() method with the optional override parameter set to TRUE.
For example
/** @var \Drupal\commerce_order\Entity\OrderItemInterface $order_item */
$order_item->setUnitPrice(new Price('10.99', 'USD'), TRUE);
Initially, the Unit price is set using the resolved price for the purchased entity (product variation). A resolved price is based on a dynamic calculation that takes into account the quantity, customer, store, and time of the request. See Price resolvers for a detailed explanation. For existing order items, Unit prices get updated during the Order refresh process. First, the resolved price is recalculated. Then, order processors can also affect the value of the price. For example, if there are any display inclusive promotions that apply to the order item, they will update the value of the Unit price. You can use the getAdjustedUnitPrice() method to get the adjusted order item unit price. This method can be useful for refunds and other purposes where there's a need to know how much a single unit contributed to the order total.
Payment prices
Payments have two Price fields: Amount and Refunded amount. The getBalance() method calculates the difference beween the Amount and the Refunded amount. These values are managed by payment gateway methods. For an overview, see the Payments documentation.
Formatting prices
The documentation page on Prices describes how a Price consists of a number and a currency code, both stored as strings. So, for example, suppose the total price for an order is "$464,230.13". That value would be stored in the database as "464230.130000" for the total price number and "USD" for the total price currency.
How exactly do we get from "464230.130000" and "USD" to the "$464,230.13" we see displayed in the order summary?
First, we determine the correct format to use for the price. This is the job of the Currency and Number format Repositories. The format specifies things like how many digits to use for the fractional part of the price and which character to use to separate the fractional part and how the currency should be displayed.
- For example, the currency pattern for US dollars specifies that the '$' symbol prefixes the price number. The ',' character separates thousands from hundreds of dollars. And the '.' character separates the dollars from the cents, with exactly 2 digits displayed for the cents. So our price should be displayed as "$464,230.13", not "463 230,130 £".
Second, we apply that Number format to the raw price data. This is the job of the Currency and Number Formatters.
Commerce Price repositories
The Commerce Price module's CurrencyRepository and NumberFormatRepository services provide the formats used by the CurrencyFormatter and NumberFormatter services.
Currency repository
The currency repository provides formats in the form of CommerceGuys\Intl\Currency\Currency value objects, loaded from the Currency entities that have been created for the site. See the Currencies documentation for a list of the Currency configuration entity properties that are loaded into the value objects. In addition, the locale property is set based on the language of the Currency entity. The repository doesn't support loading currencies in a non-default locale, since it would be imprecise to map $locale to Drupal's languages.
Number format repository
The number format repository service constructs a CommerceGuys\Intl\NumberFormat\NumberFormat value object for a given locale. These value objects have the following properties:
| Property | ID | Description | Example value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Locale | locale | The locale. | 'en_US' |
| Decimal pattern | decimal_pattern | The number pattern used to format decimal numbers. | '#,##0.###' |
| Percent pattern | percent_pattern | The number pattern used to format percentages. | '#,##0%' |
| Currency pattern | currency_pattern | The number pattern used to format currency amounts. | '¤#,##0.00' |
| Accounting currency pattern | accounting_currency_pattern | The number pattern used to format accounting currency amounts. | '¤#,##0.00;(¤#,##0.00)' |
| Numbering system | numbering_system | The numbering system, one of Arabic-Indic, Extended Arabic-Indic, Bengali, Devanagari, or Latin. Default is Latin. | 'latn' |
| Decimal separator | decimal_separator | The decimal separator. The default is '.'. |
',' |
| Grouping separator | grouping_separator | The grouping separator. The default is ','. |
' ' |
| Plus sign | plus_sign | The plus sign. The default is '+'. |
'+' |
| Minus sign | minus_sign | The minus sign. The default is '+'. |
'-' |
| Percent sign | percent_sign | The percent sign. The default is '%'. |
'٪' |
The number format definitions are specified directly in the CommerceGuys\Intl\NumberFormat\NumberFormatRepository::getDefinitions() method.
For example, here is the definition for for the default 'en' locale
'en' => [
'numbering_system' => 'latn',
'decimal_pattern' => '#,##0.###',
'percent_pattern' => '#,##0%',
'currency_pattern' => '¤#,##0.00',
'accounting_currency_pattern' => '¤#,##0.00;(¤#,##0.00)',
],
How can I alter the number format definition for a locale?
The NumberFormatDefinitionEvent event can be used to customize the number format definition for any locale. The event is dispatched by the Commerce Price NumberFormatterRepository service after the number format definition is proccessed by the CommerceGuys\Intl\NumberFormat\NumberFormatterRepository service.
For example, the format definition for the German ('de') locale specifies that ',' should be used for the decimal separator, and '.' should be used for the grouping separator. Suppose you'd like to switch those for your site. Here's an example event subscriber that does that.
Example
<?php
namespace Drupal\custom_module\EventSubscriber;
use Drupal\commerce_price\Event\PriceEvents;
use Drupal\commerce_price\Event\NumberFormatDefinitionEvent;
use Symfony\Component\EventDispatcher\EventSubscriberInterface;
/**
* Modifies the number format definition for the 'de' locale
*/
class NumberFormatDefinitionEventSubscriber implements EventSubscriberInterface {
public static function getSubscribedEvents() {
$events[PriceEvents::NUMBER_FORMAT][] = ['onNumberFormat'];
return $events;
}
public function onNumberFormat(NumberFormatDefinitionEvent $event) {
$definition = $event->getDefinition();
if ($definition['locale'] == 'de') {
$definition['decimal_separator'] = ',';
$definition['grouping_separator'] = '.';
$event->setDefinition($definition);
}
}
}
Don't forget to include a service definition for your Event Subscriber in your custom module's services.yml file and clear caches.
Commerce Price formatters
The Commerce Price module's CurrencyFormatter and NumberFormatter services extend Internationalization Library services of the same names to provide better defaults. The locale is set to the current locale, based on the current country and language for the Drupal user. The default locale is 'en'. And for the currency formatter, the maximum fraction digits is set to 6 (the storage max), and the rounding mode is set to 'none', to show prices as-is.
- The Currency formatter service is used by the Default and Calculated field formatters to display prices. (See the Displaying prices documentation.) The Currency formatter uses both the Currency repository and the Number format repository.
- The Number formatter service is used by the Number form element to support language-specific input. The Number formatter uses only the Number format repository. A raw number value, like "464230.130000", is formatted into the language-specific format on element display. It uses text for the form element instead of a number type to accept language-specific input, such as commas. During element validation the input is converted back into to the generic format, to allow the returned value to be stored.
Both formatters rely on the logic provided by the CommerceGuys\Intl\Formatter\FormatterTrait trait to format numbers using locale-specific patterns.
Displaying prices
The Commerce Price module provides three field formatters and a custom Twig filter that can be used to display Price fields.
Field formatters
The Plain price formatter
The Plain price formatter displays the price using the commerce_price_plain theme hook. It does not use locale-specific patterns for formatting prices. Instead, it simply provides the Price number string and currency Drupal\commerce_price\Entity\Currency entity values for use in the template. The default commerce_price_plain.html.twig template formats the Price as a number with 2 decimal places followed by the 3-character currency code:
{{ number|number_format(2, '.', ',') }} {{ currency.currencyCode }}
It produces output that looks like this: 10.25 USD.
This formatter can be useful for exported data (CSV). It can also be useful if you want to display Prices with a non-standard number of decimal places. For example, if you sell products in bulk in large quantities with small unit prices, you might need more than 2 decimal places.
Example
Example: suppose you sell 12,000,000 units of SKU LWS00633 for a total price of $27,600.00, and you need to display the unit price as 0.0023. To do this, you can override the default Plain price formatter template with a custom one:
{{ number|number_format(4, '.', ',') }}
The Default price formatter
The Default price formatter uses the Currency formatter service to render a given Price value object based on its currency definition. It offers two configuration options:
- Strip trailing zeroes after the decimal point.
- Currency display.
- Symbol (e.g. "$")
- Currency code (e.g. "USD")
- None
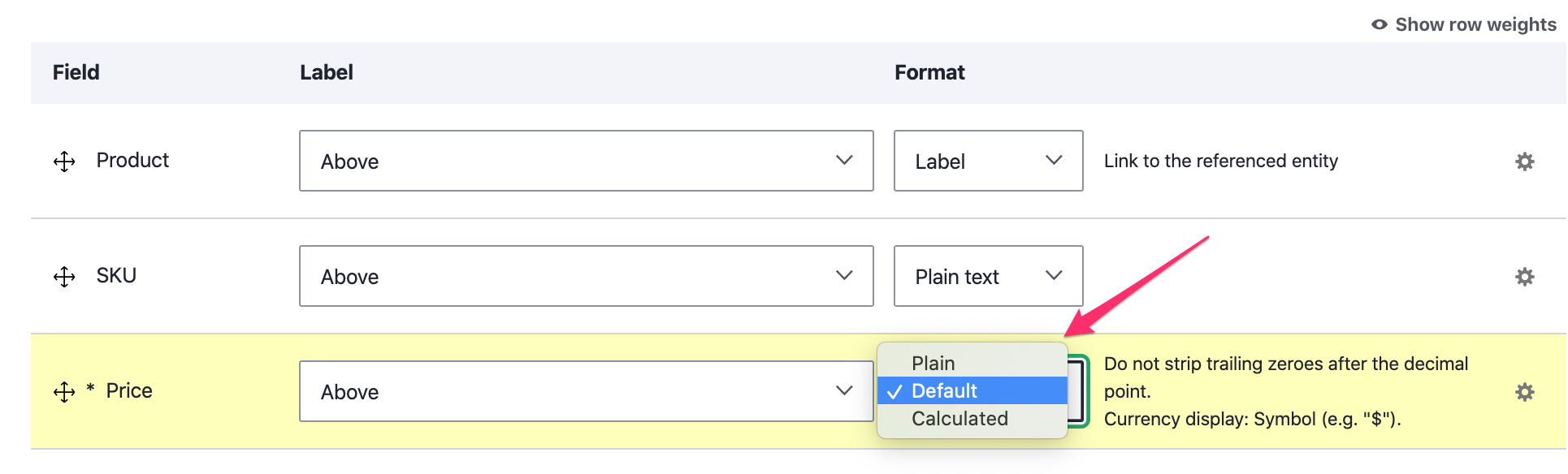
The Calculated price formatter
Like the Default price formatter, the Calculated price formatter also displays a Price formatted for its currency and offers the same Strip trailing zeroes and Currency display configuration options. Additionally, it uses Price resolving and can optionally apply other Adjustments (like promotions or taxes) to the resolved price. The Calculated price formatter can only be used for Price fields on entities that implement the PurchasableEntityInterface, such as Product variations.
Drupal Commerce actually provides two different implementations for this Price field formatter. A basic implementation is provided by the Commerce Price module. If the Commerce Order module is installed, then that basic implementation is replaced by one provided by Order module that uses the Price Calculator service to calculate the price a purchasable entity would have if it was in an order.
Calculated price formatter - Price module version
This formatter uses the ChainPriceResolver service to resolve the value of the price dynamically. It uses a quantity of 1, the current user, and the current store as the context for the price resolver. See the Price resolvers documentation to learn how Price resolvers calculate price values. Once the value is calculated, the formatter uses the Currency formatter service to render the Price based on its currency definition.
Calculated price formatter - Order module version
The Order module version Price formatter provides all the functionality of the Price module version plus configuration options for applying adjustments. The field formatter can be configured to include any of the adjustment types defined for the site. If no adjustments are selected, the Order module version of the Calcualated price formatter behaves identically to Price module version.
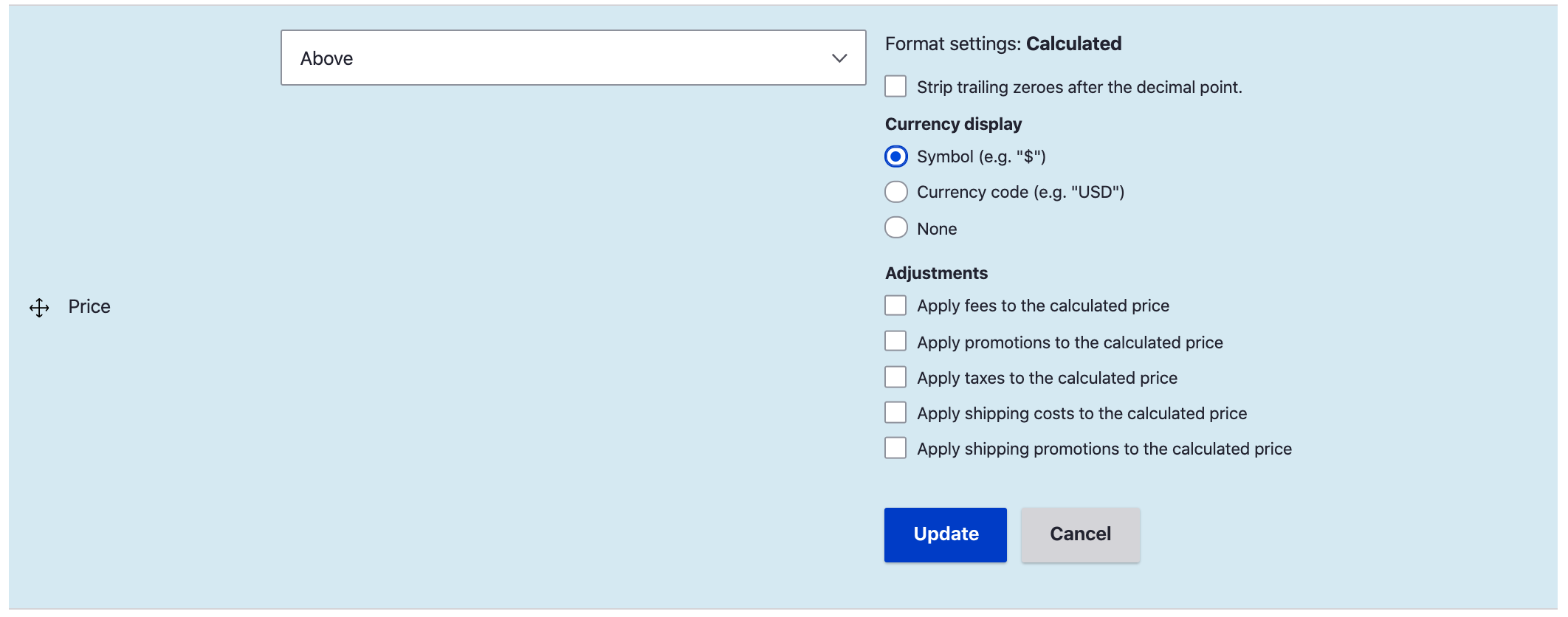
The Calculated price formatter uses the PriceCalculator service provided by the Order module to calculate the value of the Price that's displayed. If any adjustment types are selected, an Order will be created (but not saved) that has a single Order item. The Order item has a quantity of 1 and the resolved price for its Unit price. Then all Order processors for the selected adjustment types process the Order, adding Adjustments when applicable. The final adjusted total price for the Order item is returned to the Calculated price formatter, where it is rendered based on its currency definition.
Rendering prices in Twig
The Commerce Price module also provides the commerce_price_format Twig filter which renders a given Price value object based on its currency definition.
Example
Here is an example of using the Twig filter by utilizing the inline_template element type.
$element['price'] = [
'#type' => 'inline_template',
'#template' => '{{ price|commerce_price_format }}',
'#context' => [
'price' => new \Drupal\commerce_price\Price('10.25', 'USD'),
],
];
This would render as $10.25.
This Twig filter can be used on both Price value objects and arrays with number and currency_code keys. It uses the Currency formatter service to render the Price based on its currency definition.
Rendering prices without Twig
The Currency formatter service can also be used independently to get a localized formatted price string for any Price object.
Here is an example for displaying, "The price is $5.95"
$currency_formatter = \Drupal::service('commerce_price.currency_formatter');
/** @var \Drupal\commerce_price\Price $price */
$price = new Price('5.95', 'USD');
$formatted_price = $currency_formatter->format($price->getNumber(), $price->getCurrencyCode());
$price_output = t('The price is @amount', [
'@amount' => $formatted_price,
]);
For advanced customization, you can set an array of additional options for the format() method. For example, the minimum_fraction_digits and maximum_fraction_digits options can be used to override the currency's standard number of fraction digits. For the complete list of options, see CommerceGuys\Intl\Formatter\CurrencyFormatterInterface.
Example
In this example, we modify the previous example to display, "The price is 5.9500", with 4 fraction digits and no currency symbol:
$formatted_price = $currency_formatter->format($price->getNumber(), $price->getCurrencyCode(), [
'minimum_fraction_digits' => 4,
'maximum_fraction_digits' => 4,
'currency_display' => 'none',
]);
Price resolvers
Whenever a price is displayed on a product page or set for an item added to a shopping cart, that price is calculated dynamically using one or more price resolvers. If your Drupal Commerce site only requires a single price per product variation (SKU), then the default price resolver is sufficient. The default price resolver simply returns the price that has been set for the product variation (or other purchasable entity).
If your pricing requirements are more complex, then you will likely need a custom price resolver. You may be able to use a contrib module that provides a price resolver. For example, the Commerce Pricelist module includes a PriceListPriceResolver price resolver that looks up the price for a purchasable entity from a list of separately stored prices. Or you may need to write your own in a custom module. For an overview of the resolver concept as well as a variety of code examples, see the Links and resources section at the end of this document. Here, we'll step through an example of creating a price resolver that provides per-store pricing for a multi-store site.
To start, let's suppose we have a table in our database named custom_store_prices that stores a price value for every store/sku combination available on our site. (See the Drupal Schema API documentation for an overview on creating custom database tables.) We'll creating a custom price resolver by implementing the PriceResolverInterface. Here is the basic structure:
<?php
namespace Drupal\my_module\Resolver;
use Drupal\commerce\Context;
use Drupal\commerce\PurchasableEntityInterface;
use Drupal\commerce_price\Resolver\PriceResolverInterface;
use Drupal\commerce_product\Entity\ProductVariationInterface;
/**
* Returns the price fetched from the custom_store_prices table.
*/
class PriceResolver implements PriceResolverInterface {
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function resolve(PurchasableEntityInterface $entity, $quantity, Context $context) {
if (!$entity instanceof ProductVariationInterface) {
return NULL;
}
}
}
The resolve() method is defined by the PriceResolverInterface and should resolve a price for the given purchasable entity. It returns \Drupal\commerce_price\Price or null.
In our example code, we check whether the purchasable entity is an instance of ProductVariationInterface so that we can safely use the product variation's getSku() method to look up the price in our custom data table.
To get the store ID for our price lookup, we'll use the $context value. Context is a value object used by price resolvers and availability checkers. It contains known global information:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| customer | The customer assigned to the cart/order or the current user if resolving a price outside the context of an order. |
| store | The store assigned to the cart/order or the current store if resolving a price outside the context of an order. |
| time | Can be set to a unix timestamp but defaults to the current time. |
| data | An array of data. For price resolvers, use $context->getData('field_name', 'price') to get the name of the field for which the price is being resolved (e.g "list_price", "price"). |
To look up a value in our custom custom_store_prices table, we'll inject the database connection service into our price resolver, like this:
/**
* The database connection.
*
* @var \Drupal\Core\Database\Connection
*/
protected $connection;
/**
* Constructs a PriceResolver object.
*
* @param \Drupal\Core\Database\Connection $connection
* The database connection.
*/
public function __construct(Connection $connection) {
$this->connection = $connection;
}
Don't forget to include the use statement for the database connection. We'll also need the Price class:
use Drupal\commerce_price\Price;
use Drupal\Core\Database\Connection;
Now we can implement the resolve() method to look up the product variation price in the custom price table:
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function resolve(PurchasableEntityInterface $entity, $quantity, Context $context) {
if (!$entity instanceof ProductVariationInterface) {
return NULL;
}
$select = $this->connection->select('custom_store_prices', 'csp')
->fields('csp', ['price'])
->condition('store_id', $context->getStore()->id())
->condition('sku', $entity->getSku());
$result = $select->execute()->fetchAssoc();
if (isset($result['price'])) {
return new Price((string) $result['price'], $context->getStore()->getDefaultCurrencyCode());
}
return NULL;
}
With our price resolver class complete, we're ready to add this service to our custom module's service file.
my_module.price_resolver:
class: Drupal\my_module\Resolver\PriceResolver
arguments: ['@database']
tags:
- { name: commerce_price.price_resolver, priority: 200 }
We've assigned a priority of 200 to our custom price resolver so that it will execute before the default price resolver with its priority of -100. If our custom resolver fails to return a price for the purchasable entity (and no other custom price resolvers exist and produce a result), then the default resolver will return whatever price is set for the purchasable entity. The default price resolver is implemented by the Drupal\commerce_price\Resolver\DefaultPriceResolver class.
Links and resources
- Understanding resolvers documentation describes several types of resolvers used within Drupal Commerce and provides an overview of how their code is structured.
- Commerce Pricelist is a contributed module that supports creating price lists for different dates, stores, individual roles or users.
- Modifying product prices in Drupal Commerce 2 for Drupal 8 has several examples of custom price resolvers.
- Drupal Commerce 2.x and sale price provides example code for creating a "sale price" price resolver.