Installation, Updating & Uninstalling
Before you begin
If you are not familiar with using Composer to manage Drupal dependencies, read Using Composer with Drupal before continuing. Since you are already using the command line, we recommend you use Drush or Drupal console for various site management operations.
If you want to avoid using Composer for site management, the Ludwig module offers a manual alternative to Composer. In the Installing section, we document Ludwig installation; however, most of the documentation assumes that you will be using Composer to manage your site. If you do decide to use Ludwig instead of Composer, please be aware that updating and maintaining your site will be more difficult. Site administrators using Ludwig need to be careful when combining modules that depend on external libraries, since there are no safeguards against incompatible library versions or overlapping requirements.
Requirements
-
Commerce 2.x currently requires Drupal 8.5.0 or newer. Generally we require each minor release, as it contains improvements that we use, or to reduce our code base.
-
If you already have a web server, make sure it satisfies Drupal 8’s requirements. The recommended memory limit is 256MB or more.
-
To properly take advantage of Drupal's configuration management system, you should always develop locally. For local development we recommend DDEV (Docker-based) or Drupal VM (Vagrant-based).
-
You will also need Composer. We recommend that you use the newest version of composer, as older versions may or may not work. Check that your version matches the version listed on getcomposer.org.
PHP requirements
-
Drupal Commerce requires that you have the bcmath extension installed.
-
If you are using Drupal VM, add the following to your configuration (change PHP version number if needed).
php_packages_extra:
- php7.1-bcmath
Links and resources
Installation
Installing Commerce to contribute back? Check out our Getting ready for development guide.
Be sure to review requirements before starting the installation process.
The following command will download Drupal 8 + Commerce 2.x with all
dependencies to the mystore folder:
composer create-project drupalcommerce/project-base mystore --stability dev
Install it just like a regular Drupal site. Commerce will be automatically enabled for you.
Tips
- The
binfolder contains any library binaries, such as Drupal Console, PHPUnit, Behat, etc. - The
webfolder represents the document root.- If you host your site on Acquia Cloud or another service that requires Drupal in a subdirectory other than
web, these instructions describe how you can relocate the docroot.
- If you host your site on Acquia Cloud or another service that requires Drupal in a subdirectory other than
- Composer commands are always run from the site root (
mystorein this case). - See the Composer template for Drupal projects README for more details.
Run these commands in the root of your website:
Download Commerce
This will also download the required libraries and modules (Address, Entity, State Machine, Inline Entity Form, Profile).
cd /path/to/drupal8
composer require "drupal/commerce"
Enable Commerce
The instructions below use Drupal Console
drupal module:install commerce_product commerce_checkout commerce_cart
Warning
Composer is the recommended way to install and maintain a site. Site administrators using Ludwig need to be careful when combining modules that depend on external libraries, since there are no safeguards against incompatible library versions or overlapping requirements.
These instructions assume you are working with an existing site. See the Drupal.org documentation on Installing Drupal 8 if you do not have an existing site.
-
Download and install the Ludwig module.
-
Download Commerce and the following 6 required modules. Do not install the modules yet.
-
Ludwig generates a listing of libraries required by those modules. The Packages page at
admin/reports/packagesprovides a download link for each missing library along with the paths where they should be placed.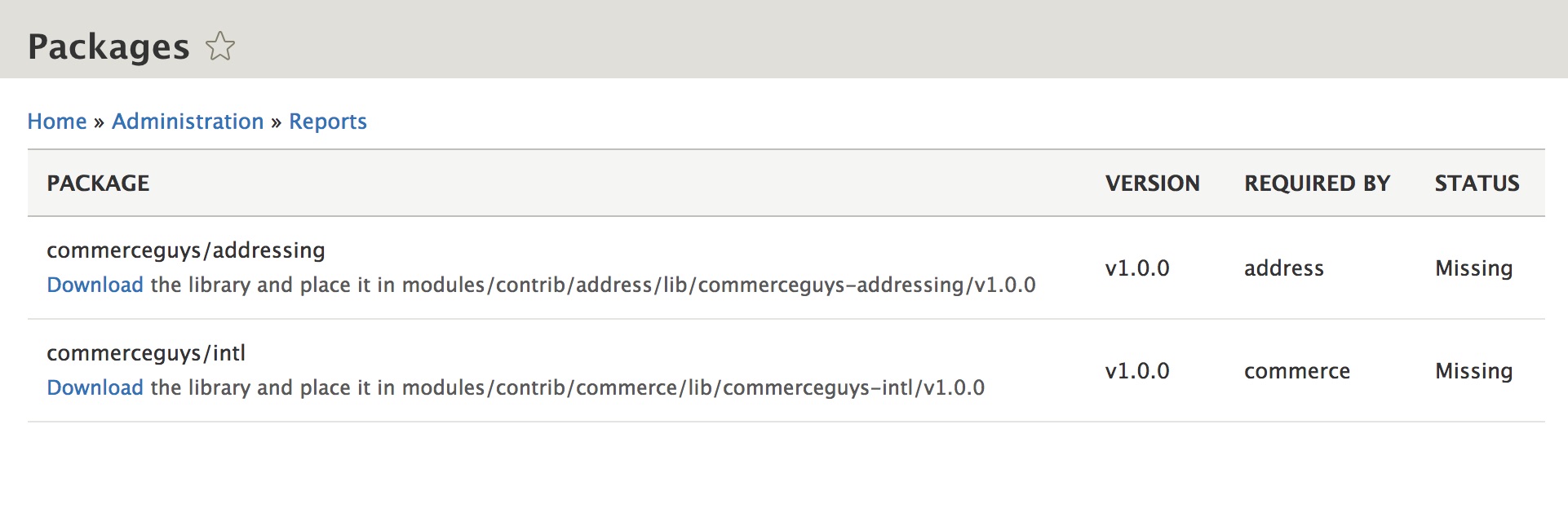
-
Download the libraries, then clear the cache to make them available. For example, download commerceguys/addressing and place it in
modules/contrib/address/lib/commerceguys-addressing/v1.0.0. You should see the STATUS for each required package change from "Missing" to "Installed". Alternatively, if you are comfortable with the command line, you can use Drupal Console or Drush commands.Drupal Console - ludwig:list: List all managed packages. - ludwig:download: Download missing packages.
Drush - ludwig-download: Download missing packages.
-
Install Commerce and the 6 required modules.
Whenever Commerce needs to be updated, all 7 modules need to be downloaded again, and then all of their libraries need to be downloaded again as well.
In subsequent sections it is assumed that you are using Composer to manage your site.
Quick start with ddev
Requirements
Create your Drupal Commerce project.
The following command will download Drupal 8 + Commerce 2.x with all
dependencies to the mystore folder:
composer create-project drupalcommerce/project-base mystore --stability dev
Configure ddev for local development.
Navigate to the project directory (which is 'mystore', unless you changed it in the above command).
Configure ddev:
cd mystore
ddev config
When prompted: - Leave the project name set to the name of your project directory (mystore). - Leave the docroot location set to 'web'. - Leave the project type set to 'drupal8'.
At this point, you can start up your project environment. However, you may want to first change the http and https ports for your site, which are set to 80 and 443 by default. If these ports are already in use on your machine, you will get the following error message:
Failed to start commerce-docs: Unable to listen on required ports, localhost port 80 is in use, Troubleshooting suggestions at https://ddev.readthedocs.io/en/latest/users/troubleshooting/#unable-listen
To change the ports used by ddev, open the file .ddev/config.yaml in your
project. Edit the router_http_port and router_https_port values and save
the file.
Start running your project:
ddev start
When the project successfully starts, you will be given the address for your
new site. For example: http://mystore.ddev.local:8080. Copy and paste your
site address into a browser.
Install Drupal 8
The first time you access your site, you will be asked for some basic
configuration information. For the database configuration, use ddev describe
to view your MySQL Credentials:
MySQL Credentials
-----------------
Username: db
Password: db
Database name: db
Host: db
Port: 3306
Host value.
Getting started
The very first thing you'll want to do to get started with Drupal
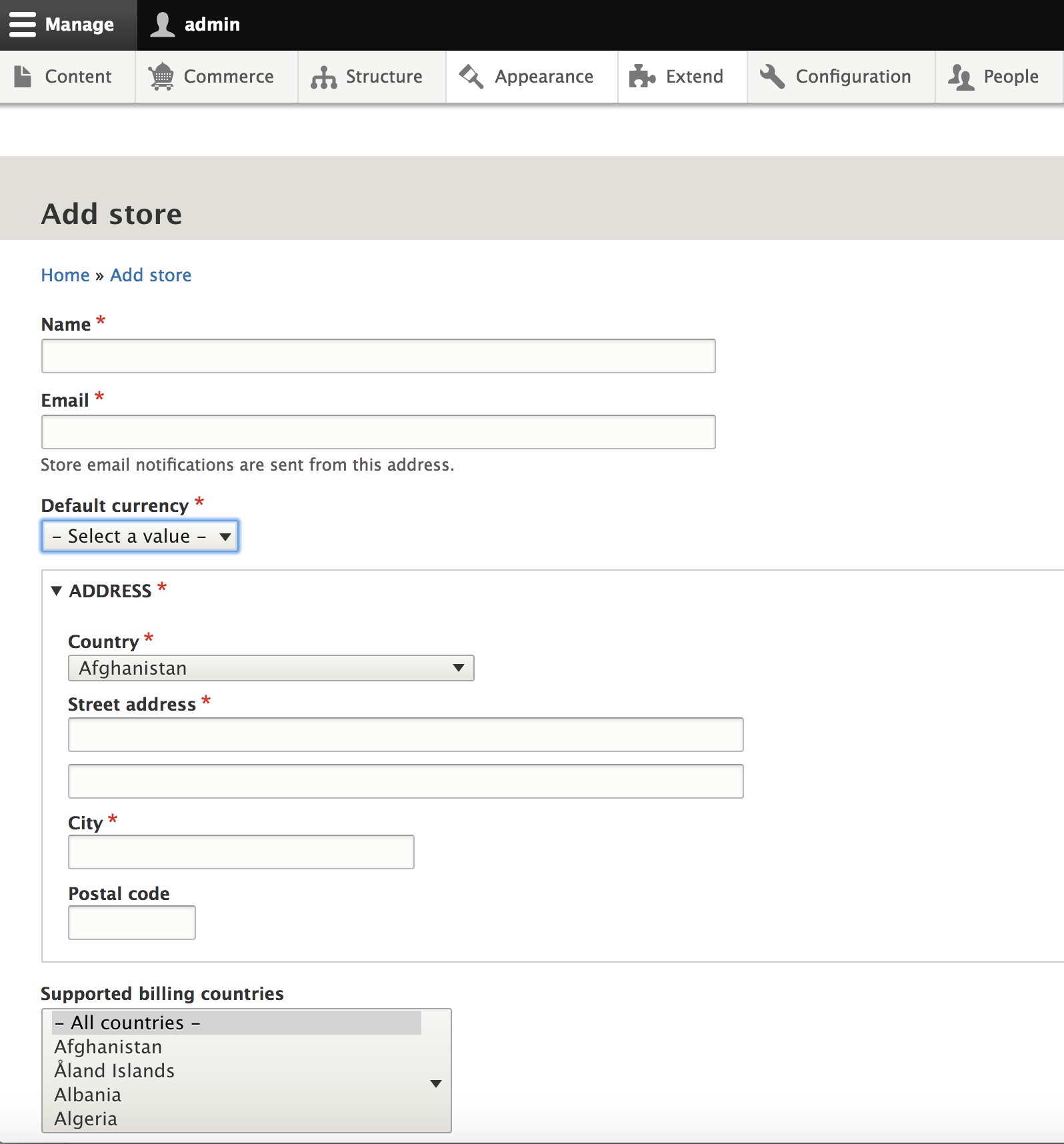
Commerce is create a store. Under the Commerce menu in the toolbar,
navigate to Configuration > Store > Stores and click the Add store button.
Once you've created a store, you'll be able to create products and start
developing the rest of your site.
Updating
Important: You must use Composer to update Drupal Core, Drupal Commerce, and all contributed modules. Otherwise, your site will break. Also, you should always back up your site before starting an update procedure. See Concept: Data Backups documentation in the Drupal 8 User Guide for more information.
It is critically important that you keep up-to-date with Drupal security advisories. You can subscribe to the "Security announcements" newsletter in your Drupal.org user profile settings.
In order to keep Drupal Commerce and your other installed modules up-to-date,
you can use Composer to produce a list of outdated modules with the Composer
outdated command:
composer outdated --direct
Then for each outdated project, you can use the Composer update command:
composer update drupal/token --with-dependencies
To update to the newest version of Drupal Commerce, you will need to update with Composer.
Due to the way Drupal.org manages package information, you need to run one of the following commands. Until Change submodule metadata to use '*' instead of 'self.version' is fixed, this is needed.
To update Drupal Commerce and all contributed projects extending Drupal Commerce:
composer update --with-dependencies "drupal/commerce*"
If you want to only upgrade Drupal Commerce, run this command:
composer update --with-dependencies drupal/commerce drupal/commerce_price drupal/commerce_product drupal/commerce_order drupal/commerce_payment drupal/commerce_payment_example drupal/commerce_checkout drupal/commerce_tax drupal/commerce_cart drupal/commerce_log drupal/commerce_store drupal/commerce_promotion drupal/commerce_number_pattern
Once the Drupal.org infrastructure issue is resolved, the command will be
composer update drupal/commerce --with-dependencies
Please note the --with-dependencies option. Without this option
specified, any needed, contributed projects and libraries will not
update. Only the Drupal Commerce module will be updated.
Run your Drupal updates once all of the dependencies are updated. We
recommend running them on the command line rather than the
update.php script. See the example below.
drupal debug:update
drupal update:execute
Composer update tips
If your composer update command isn't working, you can try:
- Run
composer why-notto check dependency issues. - Run
composer removethencomposer requireto reinstall the project. - Delete the
composer.lockfile and entire /vendor directory from your project and then runcomposer install. - Run
composer clear-cache. - Run
composer self-update.
Drupal uses a patch system to provide solutions to issues in between version releases. If you are unfamiliar with the concept of patching, you can learn about Patches at drupal.org and check our patches documentation
Extending
One of the primary strengths of both Commerce and Drupal is that they are open source projects. There is a large, active community of developers who contribute to these and related projects. As a result, you will find that it's easy to extend Commerce with freely available, "contributed" modules. And if you can't find something to meet your needs, you can always create your own modules as well. Contributed modules as well as extensive documentation about extending your Drupal site can be found on drupal.org. A good place to start is Extending Drupal 8.
For Commerce, you can find everything from modules that provide major types of functionality to smaller modules that provide unique, specialized functionality. For example:
- Commerce Shipping makes it possible to ship physical products to your customers.
- Commerce Recurring makes it possible to provide subscriptions and recurring billing.
Extending your composer-managed site with additional modules is a straightforward process. Each Drupal module has its own project page on drupal.org with information and instructions. To add a module using composer, the command is:
composer require drupal/commerce_shipping --prefer-dist
Where commerce_shipping is the name of the module you want to add to your
project. Composer will add the module as well as all of its dependencies.
Then you can install the module using the Admin UI (/admin/modules) or Drupal console:
The instructions below use Drupal Console
drupal module:install commerce_shipping
Adding custom modules from GitHub
Many Drupal developers use GitHub for their initial module development work. So you may find that a module you'd like to use to extend your site is available on GitHub but not on Drupal.org. So how do you add that custom module to your composer-managed site? You can use Composer Installers, a multi-framework composer library installer. Please see How to download a module hosted on GitHub via composer.json? on Drupal Answers for a good example of how to do this.
If you are developing custom modules locally yourself, see Managing dependencies for a custom product for an explanation of using Composer to manage your dependencies.
Uninstalling
In order to completely remove Commerce from your Drupal site, you will first
need to delete all existing data. You can do this through the Admin UI using
the Extend toolbar item and then clicking on the Uninstall tab.
Type 'commerce' into the text box at the top of the page to filter the list by Commerce modules.
Scan through the list for items that say:
There is content for the entity type:
Click the provided link to permanently remove the content for each entity type.
For example, if you have created a Store for your site, you will see:
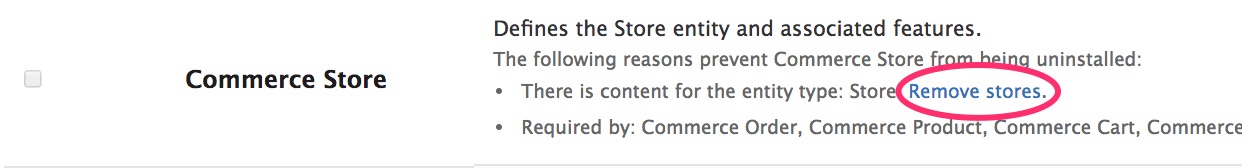
Click the Remove stores link.
Once all content has been removed, you can start uninstalling the commerce modules. You will only be able to uninstall a few at a time because of dependencies. For example, you will not be able to uninstall the base Commerce module until all other commerce modules are uninstalled. Note: if you have extended your Drupal Commerce site with any modules that are dependent upon Commerce, those modules will also need to be uninstalled before you are able to uninstall Commerce.
Here you can see boxes checked for 5 of the Commerce modules which can be
uninstalled. After clicking the Uninstall button, it will be possible to
uninstall additional modules.
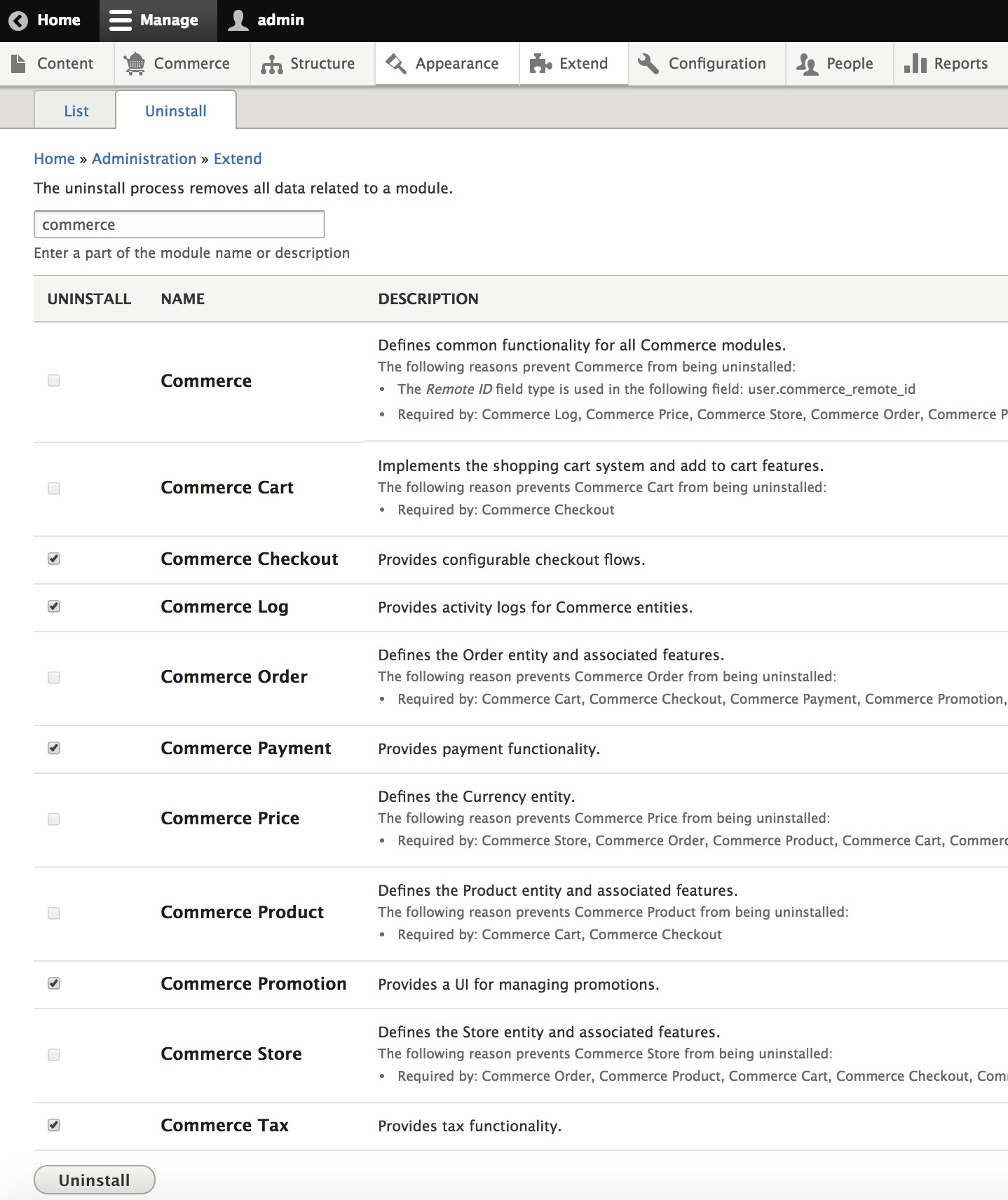
Since the Commerce base module provides a field type, it cannot be uninstalled together with the other modules. This is a known Drupal limitation. You will be blocked from uninstalling Commerce and see a "Fields pending deletion" message. You can delete the field in question by running Cron. You can run Cron through the Admin UI by navigating to Configuration > System > Cron.
Once all Commerce modules have been uninstalled, use Composer to remove the Commerce dependency from your project.
composer remove drupal/commerce
At this point, Commerce and all its data have been uninstalled from your Drupal site.
Patching
Drupal uses a patch system to provide solutions to issues in between version releases. If you are unfamiliar with the concept of patching, you can learn about Patches at drupal.org.
-
If you used
composer create-projectto create your site, you can use Composer to apply patches by modifying thecomposer.jsonfile that's at the root of your project. -
If you did not use
composer create-projectto create your site, you can use the Applying patches documentation provided by drupal.org to learn about patching options.
The following documentation describes the procedure for applying patches for a composer-managed site.
In the "extra" section of your composer.json file, you will see "installer-types" and "installer-paths". To add patches to your project, add a
new "patches" group to "extra".
For example, your "extra" section looks something like this without any patches:
"extra": {
"installer-types": [
"bower-asset",
"npm-asset"
],
"installer-paths": {
"web/core": [
"type:drupal-core"
],
"web/libraries/{$name}": [
"type:drupal-library",
"type:bower-asset",
"type:npm-asset"
],
"web/modules/contrib/{$name}": [
"type:drupal-module"
],
"web/profiles/contrib/{$name}": [
"type:drupal-profile"
],
"web/themes/contrib/{$name}": [
"type:drupal-theme"
],
"drush/contrib/{$name}": [
"type:drupal-drush"
]
}
}
Then suppose you want to apply a patch for a Drupal Commerce Issue: Issue #2901939: Move variations form to its own tab
-
Copy the link address for the patch you want to apply. In this case, the link address for the patch is
https://www.drupal.org/files/issues/2018-05-18/commerce-product-variations-tab-2901939-40.patch -
Make the following addition to the "extra" section of your composer.json file:
"patches": {
"drupal/commerce": {
"2901939: Move variations form to its own tab": "https://www.drupal.org/files/issues/2018-05-18/commerce-product-variations-tab-2901939-40.patch"
}
}
Note that "drupal/commerce" is the project name. Then for that project, you provide the specific patch information. If you have multiple patches, the "extra" section of your composer.json file should look something like this:
"extra": {
"installer-types": [
"bower-asset",
"npm-asset"
],
"installer-paths": {
"web/core": [
"type:drupal-core"
],
"web/libraries/{$name}": [
"type:drupal-library",
"type:bower-asset",
"type:npm-asset"
],
"web/modules/contrib/{$name}": [
"type:drupal-module"
],
"web/profiles/contrib/{$name}": [
"type:drupal-profile"
],
"web/themes/contrib/{$name}": [
"type:drupal-theme"
],
"drush/contrib/{$name}": [
"type:drupal-drush"
]
},
"patches": {
"drupal/commerce": {
"2901939: Move variations form to its own tab": "https://www.drupal.org/files/issues/2018-05-18/commerce-product-variations-tab-2901939-40.patch"
},
"drupal/core": {
"2904908: Fetch User ID from route context views' contextual filter for any entity": "https://www.drupal.org/files/issues/fetch_user_id_from_route_for_all-2904908-13.patch"
},
"drupal/serial": {
"2946075: Support migrating existing values": "https://www.drupal.org/files/issues/2946075-2.serial.Support-migrating-existing-values.patch"
}
}
}
Once you've made the changes to composer.json, you can apply the patch by running:
composer update drupal/commerce